C/SiC Carbon-Ceramic Composite Materials
Key Features & Advantages
-
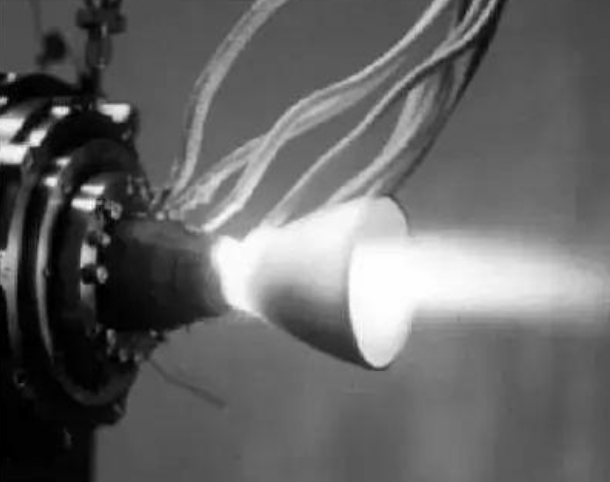
Thermal Stability:
Interface design (e.g., alternating PyC/SiC layers) and matrix modification help reduce thermal expansion and suppress microcracks, ensuring dimensional stability at high temperatures. -
Oxidation Resistance:
Ceramic coatings such as SiC and HfC effectively block oxygen diffusion, providing oxidation protection even above 2200°C. -
Friction Performance:
Stable friction coefficient and low wear rate at temperatures over 1000°C, ideal for braking systems under extreme conditions.
Manufacturing Technology
-
Preform Construction:
-
Conventional: Needle-punched or stitched fiber preforms form porous C/C bodies via CVI, followed by SiC matrix introduction through RMI.
-
Additive Manufacturing: Uses laser sintering or digital light processing to create short-fiber reinforced preforms, simplifying complex shapes and reducing costs.
-
-
Densification Methods:
-
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Deposits PyC interface and SiC matrix for stronger bonding.
-
PIP (Precursor Infiltration & Pyrolysis): Repeated impregnation and pyrolysis with SiC precursor reduces porosity.
-
RMI (Reactive Melt Infiltration): Molten silicon reacts with carbon to rapidly form a dense SiC matrix.
-
Applications
-
Aerospace:
Thermal protection systems (e.g., nose cones, panels) and brake components; used in Porsche brake discs and heavy-duty truck pads. -
Rail Transit:
Maglev train skids and high-speed train brake pads; replaces metal to reduce weight and improve durability. -
Defense & Military:
Ultra-high-temperature oxidation-resistant parts for hypersonic vehicles; long-term protection above 2200°C with HfC/ZrB₂ coatings.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.